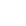
From the Amazon to the World: How Açaí is Grown and Exported Sustainably
- Rio Açaí

- Mar 21, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Mar 24, 2025
Açaí, the small purple fruit native to the Amazon, has taken the world by storm with its unique flavor and numerous health benefits. However, behind every açaí bowl or smoothie enjoyed worldwide lies a complex process of cultivation, harvesting, and exportation. More than just a product, açaí is a symbol of Amazonian biodiversity and an example of how sustainable production can benefit both the local economy and the environment.

Açaí Cultivation: A Gift from the Rainforest
Açaí grows on palm trees native to the Amazon region, primarily in Brazil. These trees can reach up to 25 meters (82 feet) in height and produce clusters of small, dark purple berries. Traditional açaí cultivation is carried out by local communities, who use sustainable techniques to harvest the fruit without harming the ecosystem.
Harvesting and Processing the Fruit
Açaí harvesting is done manually, with skilled workers climbing the tall palm trees to cut the fruit clusters. Once harvested, the berries go through a rigorous process to ensure quality and freshness:
Washing and selection – Only the freshest and healthiest berries are used.
Pulp extraction – The açaí is mashed, and the pulp is separated from the seed.
Freezing or pasteurization – This helps preserve nutrients and allows the fruit to be transported worldwide.
This process ensures that açaí reaches consumers with its flavor and nutritional value intact, whether in frozen pulp, powder, or as an ingredient in various products.
Sustainability in Açaí Production
Açaí production is considered environmentally friendly because:
It prevents deforestation – Since açaí palm trees grow naturally in the rainforest, no trees need to be cut down for planting.
It supports local communities – Thousands of families rely on açaí harvesting as their primary source of income.
It preserves biodiversity – Traditional açaí production helps maintain the balance of the Amazon ecosystem.
Additionally, several initiatives aim to make production even more sustainable by promoting responsible water use, recycling açaí waste, and fair trade practices to ensure that farmers receive fair wages for their work.
Açaí Export and Its Global Popularity
Over the past few decades, demand for açaí has skyrocketed, especially in the United States, Europe, and Canada. Its reputation as a superfood rich in antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats has fueled its consumption in smoothies, bowls, and even nutritional supplements.
To meet this growing demand, exporters adhere to strict quality and food safety standards, ensuring that açaí reaches consumers without losing its nutritional properties.
Conclusion
Açaí is more than just a trendy food—it is a fruit that embodies the richness of the Amazon rainforest and supports thousands of families. With responsible cultivation practices and sustainable exportation, Brazil is not only sharing this natural treasure with the world but also contributing to environmental conservation.
Whether in Brazil or Canada, every açaí bowl tells a story of tradition, sustainability, and delicious flavor!